Do you want to become an aeronautical maintenance technician but don’t know which category to choose?
In the Spanish territory, there are about 15 centers where you can study the different types of Aeronautical Maintenance licenses, the most popular being A, B1(B1.1, B1.3), and B2.
Aeronautical Maintenance License Category A
A category A aircraft maintenance license is useful for maintenance work on line or directly with the aircraft at the airport. This license allows its holder to issue certificates of release to service following secondary scheduled maintenance work and simple defect rectifications, within the task limits specifically defined in the authorization. The powers of certification are limited to work performed personally by the licensee.
Category A is divided into the following subcategories:
- Subcategory A1: Turbine engine airplanes
- Subcategory A2: Aeroplanes with piston engine
- Subcategory A3: Turbine-engine helicopters
- Subcategory A4: Piston-engine helicopters
To apply for a category A license the student must have passed all relevant examinations for category A or B in its different subcategories and demonstrate:
- One year of practical experience in operational aircraft maintenance if the applicant has completed a basic training course in a Part-147 organization.
- Two years of practical experience in the maintenance of operational aircraft if the applicant has training considered relevant by EASA.
- Three years of practical experience in the maintenance of operational aircraft if the applicant does not have relevant technical training.
Aeronautical Maintenance License Category B1
A category B1 aircraft maintenance license allows its holder to issue certificates of release to service following maintenance work, including work on the aircraft structure, powerplant, and mechanical and electrical systems. Also included in these faculties is the replacement of on-line replaceable avionics units that require simple checks to demonstrate their operation. Category B1 automatically includes the corresponding subcategory A.
Category B1 is divided into the following subcategories:
- Subcategory B1.1: Aircraft with turbine engine
- Subcategory B1.2: Aeroplanes with piston engines
- Subcategory B1.3: Turbine-engine helicopters
- Subcategory B1.4: Piston-engine helicopters
To apply for a category B1 license the student must have passed all relevant exams for category B1 in its different subcategories and demonstrate:
- Two years of practical experience in operational aircraft maintenance if the applicant has completed a basic training course in a Part-147 organization.
- Three years of practical experience in the maintenance of operational aircraft if the applicant has training considered relevant by EASA.
- Five years of practical experience in the maintenance of operational aircraft if the applicant does not have relevant technical training.
- For subcategories B1.2 and B1.4, the experience required is the same as for category A.
Aeronautical Maintenance License Category B2
A category B2 aircraft maintenance license allows its holder to issue certificates of release to service following maintenance work on electrical and avionics systems. Electrical and avionics tasks on powertrains as well as mechanical systems require only simple checks to demonstrate operation. Issue fitness-for-service certificates after secondary scheduled line maintenance work and simple defect rectifications. This certification authority is restricted to the tasks that the holder has personally carried out in the maintenance organization that issued the certification authorization and to the ratings already noted on the B2 license.
To apply for a category B2 license, the student must have passed all the exams corresponding to that category and demonstrate the same years of experience required for category B1.
Category B2 does not include any subcategory and can be valid for both large and small aircraft such as airplanes and helicopters.
Aeronautical Maintenance License Category C
A category C aircraft maintenance license allows its holder to issue certificates of release to service following maintenance work on the aircraft. The powers apply to the aircraft as a whole including all systems in a Part 145 organization. Category C personnel who also hold category B1 or B2 qualifications may perform both functions in base maintenance.
To apply for the category C license you must demonstrate at least:
In relation to large aircraft
- Three years of experience exercising B1.1, B1.3 or B2 powers on large aircraft or as B1.1, B1.3 or B2 support staff in accordance with Part-145.
- Five years of experience exercising B1.2 or B1.4 powers or as B1.2 or B1.4 support staff in accordance with Part 145.
With respect to non-large aircraft
- Three years of experience in the exercise of B1 or B2 category powers on non-large aircraft or as support staff under part 145 B1 or B2.
Obtained by academic means
- An applicant possessing an academic degree in a technical discipline from a university or other institution of higher education approved by the competent authority, three years of experience working in a civil aircraft maintenance environment performing a representative set of duties directly related to aircraft maintenance, including six months of base maintenance observation work.
Requirements for adding a new category to the aeronautical maintenance license.

In case you are in possession of an aeronautical maintenance license and you wish to add another category, it will be necessary to take the exams required for the new category and meet the minimum experience to apply for the inclusion of the new category in the maintenance license.
Below you will find a basic experience table to add a new category to the maintenance license.
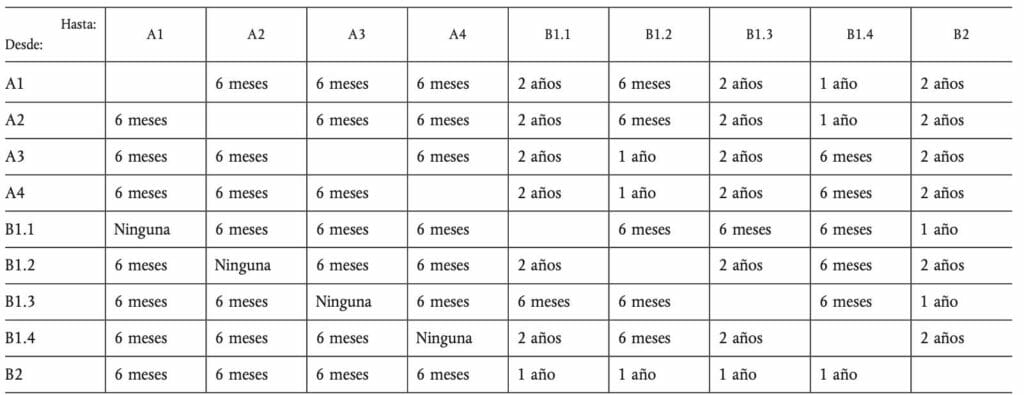
Other specialties and job categories in aeronautical maintenance.
Other categories not mentioned above, but in great demand in the aeronautical sector are Structural Repair Specialist and Non-Destructive Testing Specialist. Both profiles require great skill, knowledge, and several courses for their development and improvement.
- Structural Repair Work Technician: The course has a duration of approximately 6 months to 1 year including internships in work centers, as with all aviation work, a high level of English is required. Its main difficulty lies in the interpretation of the structural diagrams, in the use of the various tools used for the repair and manufacture of the different metallic parts of the aircraft. It is essential to know how to interpret the structural diagrams and repair-evaluation manuals of the aircraft’s metal parts. By specializing as a Metal Structures Assembler and Repair Technician you will be able to find work without much difficulty (depending on your aptitudes and skills on the job) as it is necessary in manufacturing, heavy maintenance and line maintenance in the Aeronautical sector. In Spain, you will find a wide variety of centers where you can train, the most popular being Seville and Madrid for their Airbus plants.
- Non-Destructive Testing Technician: What is Non-Destructive Testing? Non-destructive testing is testing that does not alter the shape or properties of an object. They do not produce any type of damage to it or the damage is practically imperceptible. This type of test is used to study the physical, chemical or mechanical properties of some materials. This course requires certification by levels which will allow the technician to use one or another type of tester for the part to be inspected. It is in great demand in the aeronautical sector, both in the manufacture and repair of aircraft metal parts.
In the aeronautical sector there is a wide variety of jobs to do, choose the one that best suits your skills and get ready to succeed in aviation.





